
Glycation, a natural process that affects our skin’s youthfulness and elasticity, plays a significant role in how our skin ages. But what exactly is glycation, and how does it influence the health and appearance of our skin? Here we unpack the science behind glycation, shedding light on how it accelerates skin aging and the visible signs it leaves behind. From wrinkles and loss of radiance to sagging skin, understanding glycation is key to combating these common signs of aging.
Contents
- The Science Behind Glycation
- Glycation and Skin Aging: The Effects
- Preventing and Mitigating the Effects of Glycation
- Advanced Glycation Treatments and Therapies
- References
The Science Behind Glycation
Glycation is a biological process that might sound complex, but its understanding is crucial in comprehending how our skin ages. Before delving into the effects of glycation on the skin, it’s essential to grasp what glycation is and the science behind it. This understanding lays the foundation for why certain lifestyle and skincare choices can make a significant difference in maintaining youthful skin.
Explanation of the Glycation Process
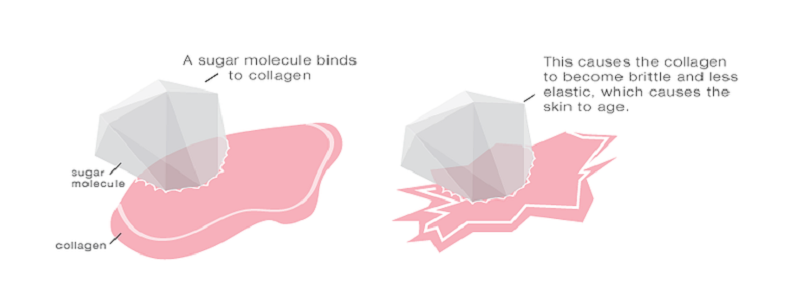
Glycation occurs when sugars, like glucose and fructose, attach themselves to proteins or lipids without the control of an enzyme. This process typically happens in our bodies over time, especially as we consume foods with high sugar content. It’s a natural part of aging, but various factors can accelerate it.
When sugars bind to proteins, they form harmful new molecules called ‘Advanced Glycation End-products’ or AGEs. The formation of AGEs is a slow and irreversible process, which, over time, accumulates and affects the body’s molecules and cells. In the context of skin health, these AGEs have a profound impact, especially on collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for maintaining the skin’s firmness and elasticity.
The Role of Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) in Skin
The formation of AGEs plays a pivotal role in the skin’s aging process. Collagen and elastin, the proteins that give skin its structure and elasticity, are particularly susceptible to glycation. As AGEs accumulate, they cause these proteins to become rigid and lose their regenerative ability.
This rigidity is problematic because collagen and elastin need to be flexible and resilient to maintain healthy, youthful skin. Once glycated, these proteins can no longer perform their functions effectively. This results in various signs of aging, such as loss of firmness, reduced elasticity, and the formation of wrinkles [1].
Connection Between Glycation and Skin Elasticity and Firmness
The relationship between glycation and skin’s elasticity and firmness is a direct one. As we age, the natural production of collagen and elastin decreases, and the existing proteins become more susceptible to damage, including glycation. The stiffening of collagen and elastin fibers due to AGEs leads to a loss of skin elasticity, making it more prone to wrinkling and sagging.
This process is not just limited to the face; it affects the entire body, though it’s most visible in areas with delicate skin, like the face and hands. Understanding this connection highlights the importance of addressing glycation in any comprehensive skincare regimen aimed at combating signs of aging.
Glycation and Skin Aging: The Effects
Glycation’s role in skin aging is both significant and multifaceted. While the science behind glycation lays the groundwork for understanding, observing its effects on the skin brings this concept into a clearer, more tangible focus. The impact of glycation manifests in various visible and tangible signs, profoundly influencing the overall appearance and health of our skin.
Acceleration of Skin Aging Due to Glycation
Glycation accelerates the natural aging process of the skin in several ways. As glycation progresses, the skin loses its youthful resilience and flexibility. This is primarily due to the stiffening of collagen and elastin, as previously discussed. Moreover, the skin’s ability to repair itself diminishes, leading to more rapid aging. This acceleration is often more pronounced in individuals with high sugar diets or those exposed to certain environmental factors that can exacerbate the effects of glycation [2].
Visible Signs of Glycation on Skin
The physical manifestations of glycation on the skin are diverse and significant. These signs are often the first indicators that glycation is occurring and affecting skin health.
Wrinkles and Fine Lines
One of the most noticeable signs of glycation on the skin is the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. As the skin’s underlying collagen and elastin fibers become more rigid due to AGEs, the skin loses its ability to bounce back, resulting in permanent lines and creases.
Loss of Radiance and Dullness
Glycated skin often appears less radiant and more dull. This is because the skin’s natural rejuvenation processes are hindered, leading to a buildup of dead skin cells and a lackluster complexion.
Sagging and Loss of Firmness
The skin’s firmness and tightness are compromised due to the degradation of collagen and elastin. This results in sagging, particularly around the jawline, under the eyes, and on the neck, where the skin is more susceptible to the effects of gravity and aging.
Internal Impact of Glycation on Skin Cells and Collagen
Beyond the visible signs, glycation has a profound internal impact on skin cells and collagen. Glycated collagen is less efficient in its interactions with other cells and molecules within the skin. This inefficiency leads to a breakdown in the skin’s support system, affecting not only its appearance but also its overall health. The skin becomes more vulnerable to external stressors like UV radiation and pollution, which can further exacerbate aging signs [3].
Preventing and Mitigating the Effects of Glycation
While the process of glycation and its effects on skin aging may seem daunting, there are effective strategies to prevent and mitigate its impact. Addressing glycation involves a combination of dietary changes, specific skincare products, and overall lifestyle adjustments. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce the effects of glycation on your skin and even slow down the aging process.
Dietary Changes to Reduce Glycation
The foods we consume play a crucial role in the glycation process. Modifying your diet can significantly impact the rate at which glycation occurs and its subsequent effects on the skin.
Foods to Avoid
Reducing the intake of high-sugar foods and refined carbohydrates is key. These foods rapidly increase blood sugar levels, leading to an increase in the formation of AGEs. Processed foods, sugary snacks, and white bread are examples of items to limit or avoid.
Beneficial Foods for Preventing Glycation
Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants can help combat the effects of glycation. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals and can reduce the formation of AGEs. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Foods high in vitamins C and E, as well as dietary supplements like carnosine, can also be beneficial.
Skincare Products and Ingredients That Counteract Glycation
In addition to dietary changes, certain skincare products and ingredients are specifically formulated to fight against the effects of glycation.
Antioxidants and Their Role
Antioxidants are vital in skincare to prevent and repair skin damage caused by glycation. Ingredients like vitamin C, vitamin E, ferulic acid, and green tea extract can provide significant benefits [4].
Specific Skincare Ingredients Effective Against AGEs
Look for products containing aminoguanidine and carnosine, which can inhibit the formation of AGEs. Retinoids, hyaluronic acid, and peptides also play a role in rejuvenating glycated skin by promoting collagen production and skin hydration.
Lifestyle Modifications to Protect Skin Health
Lastly, lifestyle plays a critical role in combating glycation.
Sun Protection
UV exposure can exacerbate the effects of glycation. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours can help protect the skin.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption
Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake can accelerate the aging process, including the effects of glycation. Reducing or eliminating these habits can significantly benefit skin health.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity improves circulation and overall health, which can help the skin repair and rejuvenate itself more effectively.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to increased sugar levels in the blood, promoting glycation. Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or even regular walks can be beneficial.

Advanced Glycation Treatments and Therapies
In addition to the preventative measures and lifestyle changes discussed earlier, there are advanced treatments and therapies specifically designed to target and combat the effects of glycation on the skin. These treatments, often available through dermatologists or specialized skincare clinics, offer more intensive solutions to those looking to reverse the signs of aging related to glycation.
Professional Skincare Treatments Targeting Glycation
Professional skincare treatments can significantly enhance your anti-glycation regimen. These treatments are typically more potent and targeted than at-home care products, offering a deeper level of skin rejuvenation.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels, which use acids to remove the outer layer of dead skin cells, can improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of damage caused by glycation. By removing the outer layer, these peels stimulate the growth of new, healthier skin cells [5].
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments can also be effective in treating skin damaged by glycation. These treatments work by delivering concentrated light to the skin, which helps to stimulate collagen production and improve overall skin texture.
Microneedling
Microneedling creates tiny punctures in the skin, which can stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture. This treatment is especially beneficial for addressing the fine lines and wrinkles that result from glycation.
LED Light Therapy
Specific wavelengths of light in LED light therapy can stimulate skin cells and reduce the effects of glycation. This non-invasive treatment can improve skin tone and texture over time.
Emerging Research and Future Therapies in Combating Glycation
The field of dermatology is continuously evolving, with new research leading to innovative treatments for skin aging due to glycation.
Topical Agents
Researchers are exploring new topical agents that specifically target the glycation process. These include advanced formulations containing compounds that can break down existing AGEs or prevent their formation.
Gene Therapy and Cellular Repair
Cutting-edge research into gene therapy and cellular repair mechanisms holds promise for reversing the effects of glycation at a molecular level. Although these therapies are still in the experimental stage, they represent a potential future where skin aging due to glycation can be significantly reversed.
Nutraceuticals
The development of nutraceuticals, which are dietary supplements designed to have a beneficial effect on skin health, is another exciting area of research. These products might target glycation from within, providing a systemic approach to skin health.
References
[1] Research Advances on the Damage Mechanism of Skin Glycation and Related Inhibitors
[2] Glycation and Skin Aging
[3] What Is Skin Glycation?
[4] Advanced Glycation End Products in the Skin: Molecular Mechanisms, Methods of Measurement, and Inhibitory Pathways
[5] Nutrition and aging skin: sugar and glycation
