
Ceramides, though less talked about than other skincare buzzwords, are fundamental building blocks of our skin’s structure. They play a crucial role in protecting our skin against environmental stressors, retaining moisture, and ensuring our skin remains supple and resilient. Here we unravel the science behind ceramides – what they are, how they function, and why they are indispensable for skin barrier health.
Contents
The Science Behind Ceramides
In the quest to understand the integral role of ceramides in skin health, it’s essential to delve into the scientific aspects. Ceramides are not just another ingredient in skincare products; they are vital components of our skin’s natural composition. By exploring their structure, formation, and function, we gain a deeper appreciation for their role in skin health.
Composition and Types of Ceramides
Ceramides are a type of lipid, or fat, naturally found in high concentrations within the cell membranes of our skin. They are composed of sphingosine, a long-chain amino alcohol, and a fatty acid, which are linked together to form a molecule. This unique structure allows ceramides to effectively lock moisture into the skin and form a protective barrier against environmental damage.
There are several types of ceramides, numbered from 1 to 9, each with a slightly different structure and function. These variations contribute to the skin’s ability to retain moisture and protect itself from irritants and pathogens. For instance, ceramide 1, also known as ceramide EOS, is known for its effective barrier-repair properties, while ceramide 3, or ceramide NP, is crucial for maintaining skin hydration.
How Ceramides are Formed in the Body
The body synthesizes ceramides through a complex process involving several steps. This process begins with the conversion of serine and palmitoyl-CoA into sphinganine, which then binds with a fatty acid to form dihydroceramide. Dihydroceramide is then converted into ceramide through the addition of a double bond.
This synthesis mainly occurs in the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin, where ceramides play a critical role in maintaining the barrier function. Age, environmental factors, and certain skin conditions can affect the body’s ability to produce ceramides, leading to a weakened skin barrier and various skin issues [1].
The Role of Ceramides in the Skin’s Lipid Barrier
Ceramides are the most crucial component of the skin’s lipid barrier, accounting for over 50% of its composition. This barrier is essential for protecting the skin from environmental aggressors like pollutants and allergens and preventing water loss. Ceramides, along with other lipids like cholesterol and free fatty acids, form a protective layer that keeps the skin hydrated and defends against external stressors.
By binding skin cells together, ceramides maintain the integrity of the skin barrier. They act like the ‘mortar’ between the ‘bricks’ (skin cells), ensuring the barrier is robust and functional. This structural role is vital for preventing transepidermal water loss, a common issue in dry and aging skin.
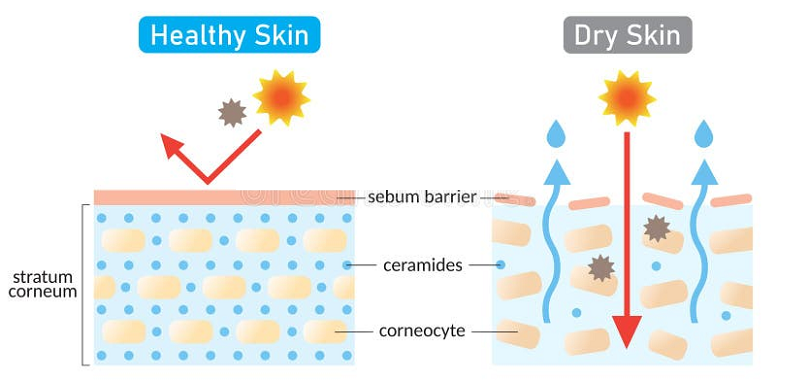
Ceramides and Skin Barrier Health
After exploring the scientific foundation of ceramides, it’s crucial to understand how they directly impact skin barrier health. The skin barrier is our first line of defense against the external environment, and ceramides are key to its effectiveness.
Ceramides Protect Against Environmental Stressors
Ceramides play a significant role in shielding the skin from environmental stressors such as pollutants, harsh weather conditions, and UV radiation. These stressors can strip away natural oils, leading to weakened skin barrier function. Ceramides help to fortify the skin’s barrier, preventing these external factors from causing damage and irritation [2].
Their lipid-rich structure forms a protective layer that limits the penetration of harmful substances while retaining essential nutrients and moisture. This barrier not only defends against immediate threats but also aids in long-term skin health by minimizing the impact of chronic exposure to environmental aggressors.
Ceramides Maintain Moisture and Preventing Dryness
One of the most notable functions of ceramides is their ability to maintain moisture in the skin. They are crucial in preventing transepidermal water loss, a process where water evaporates from the skin’s surface, leading to dryness and irritation.
Ceramides work by creating a seal that traps moisture in the skin, ensuring it remains hydrated and plump. This is particularly important for individuals with dry or aging skin, where natural ceramide levels may be depleted. By maintaining proper hydration, ceramides help to keep the skin looking smooth, supple, and youthful.
Ceramides Contribute to Skin Elasticity and Texture
Ceramides also contribute significantly to the skin’s elasticity and texture. A healthy skin barrier supported by adequate ceramide levels is more resilient and can bounce back from stretching and stress more effectively. This elasticity reduces the likelihood of developing fine lines and wrinkles, which are often signs of a compromised skin barrier.
Furthermore, ceramides help in smoothing the skin’s texture. They ensure that the skin’s surface is even and soft, addressing issues like rough patches and flakiness. Consistent hydration and protection offered by ceramides result in a more even, radiant complexion [3].
Common Skin Issues Linked to Ceramide Deficiency
Understanding the role of ceramides in maintaining skin health leads to a crucial question: what happens when the skin lacks these essential lipids? Ceramide deficiency can lead to various skin issues, often characterized by increased sensitivity, dryness, and irritation.
Eczema and Dermatitis
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is one of the most common skin conditions linked to ceramide deficiency. This condition is marked by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Studies have shown that individuals with eczema often have lower levels of ceramides in their skin, which weakens the skin barrier and makes it more susceptible to irritants and allergens.
By compromising the skin’s natural barrier, a deficiency in ceramides leads to increased water loss and decreased ability to fend off environmental triggers. This results in the typical symptoms of eczema, such as dryness, itching, and redness. Replenishing ceramide levels, either through topical treatments or dietary changes, can help restore the skin’s barrier and alleviate the symptoms of eczema.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is another skin condition that can be exacerbated by a lack of ceramides. Characterized by rapid skin cell turnover leading to thick, scaly patches, psoriasis is not only a physical but also a psychological burden for many. While the exact relationship between ceramides and psoriasis is complex, research suggests that ceramide deficiency may play a role in the skin’s abnormal response.
Psoriasis lesions have been found to have altered ceramide composition, which may contribute to the compromised barrier function seen in psoriatic skin. By strengthening the skin barrier through ceramide-rich treatments, it may be possible to reduce the severity and frequency of psoriasis flare-ups [4].
Age-Related Dryness and Wrinkling
As we age, our skin naturally produces fewer ceramides, leading to increased dryness and the formation of wrinkles. This age-related ceramide loss contributes to a weakened skin barrier, making older skin more prone to dehydration and environmental damage.
The decrease in ceramides affects the skin’s ability to retain moisture, leading to a loss of firmness and elasticity. This, in turn, makes fine lines and wrinkles more pronounced. Incorporating ceramide-based products into skincare routines can help replenish the lost lipids, improving hydration, reducing the appearance of wrinkles, and restoring a more youthful complexion.
Enhancing Ceramide Levels
Recognizing the importance of ceramides in skin health naturally leads to exploring ways to enhance ceramide levels in the skin. Whether due to aging, environmental factors, or specific skin conditions, boosting ceramide levels can significantly improve skin barrier function and overall skin health.
Dietary Sources of Ceramides
Diet plays a significant role in skin health, and certain foods are known to be rich in ceramides or stimulate the body’s natural production of these lipids. Foods that are particularly beneficial include:
- Whole grains like wheat, corn, and brown rice, which contain natural ceramides.
- Soybeans, known for their skin-hydrating properties.
- Dairy products, especially cheese and milk, which have ceramide precursors.
- Eggs, which contain lecithin, a substance that helps the body synthesize ceramides.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help naturally boost your skin’s ceramide levels, enhancing its ability to retain moisture and protect against environmental stressors.
Topical Ceramide-Enriched Skincare Products
Topical application of ceramides is one of the most direct ways to replenish these crucial lipids in the skin. A wide range of skincare products, such as creams, lotions, and serums, are formulated with synthetic or naturally-derived ceramides. These products work by supplementing the skin’s natural ceramide content, strengthening the barrier function and improving hydration [5].
When selecting ceramide-enriched skincare products, look for those that also contain other barrier-repairing ingredients like cholesterol and fatty acids, which work synergistically with ceramides to maximize skin barrier repair.
The Role of Supplements
In addition to diet and topical treatments, ceramide supplements can also be an effective way to enhance ceramide levels. These supplements are usually derived from plant sources like wheat or rice and are designed to increase the body’s ceramide production from within.
While research on the effectiveness of ceramide supplements is still evolving, some studies suggest they can improve skin hydration and barrier function. As with any supplement, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a ceramide supplement regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking other medications.
References
[1] Ceramides for skin: Benefits, side effects, and more
[2] Ceramides and skin function
[3] The Importance of a Healthy Skin Barrier From the Cradle to the Grave Using Ceramide-Containing Cleansers and Moisturizers
[4] Ceramides 101: A Detailed Guide
[5] What Are Ceramides?
